寵物小知識
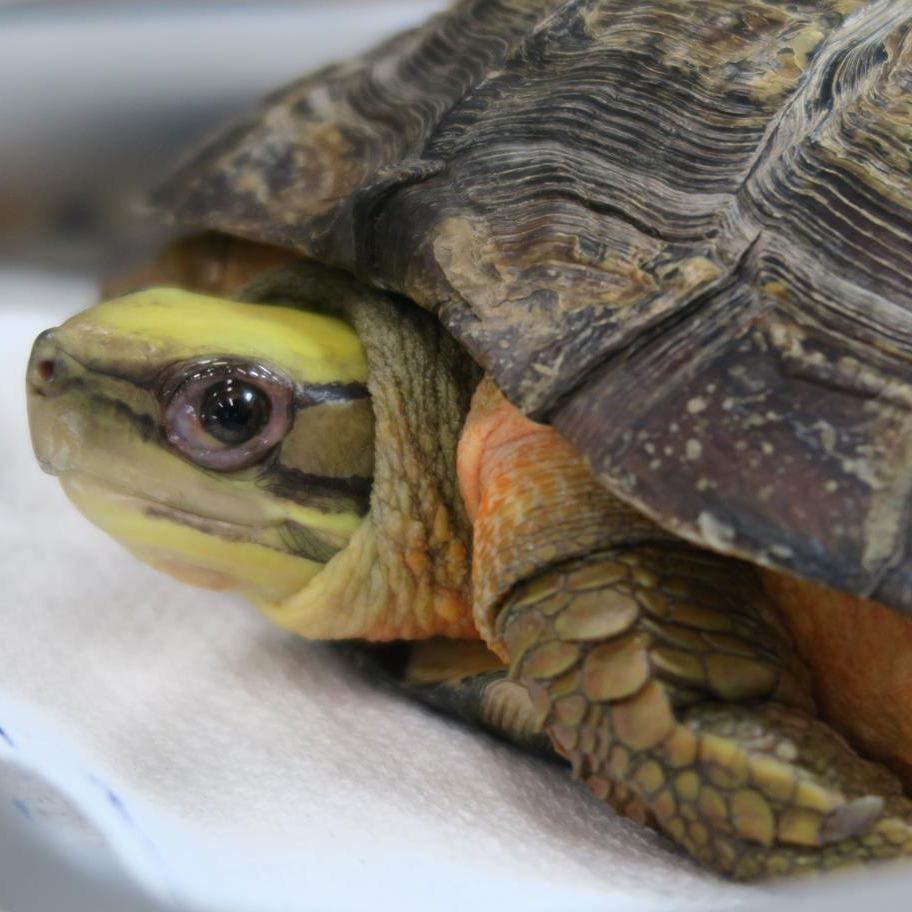

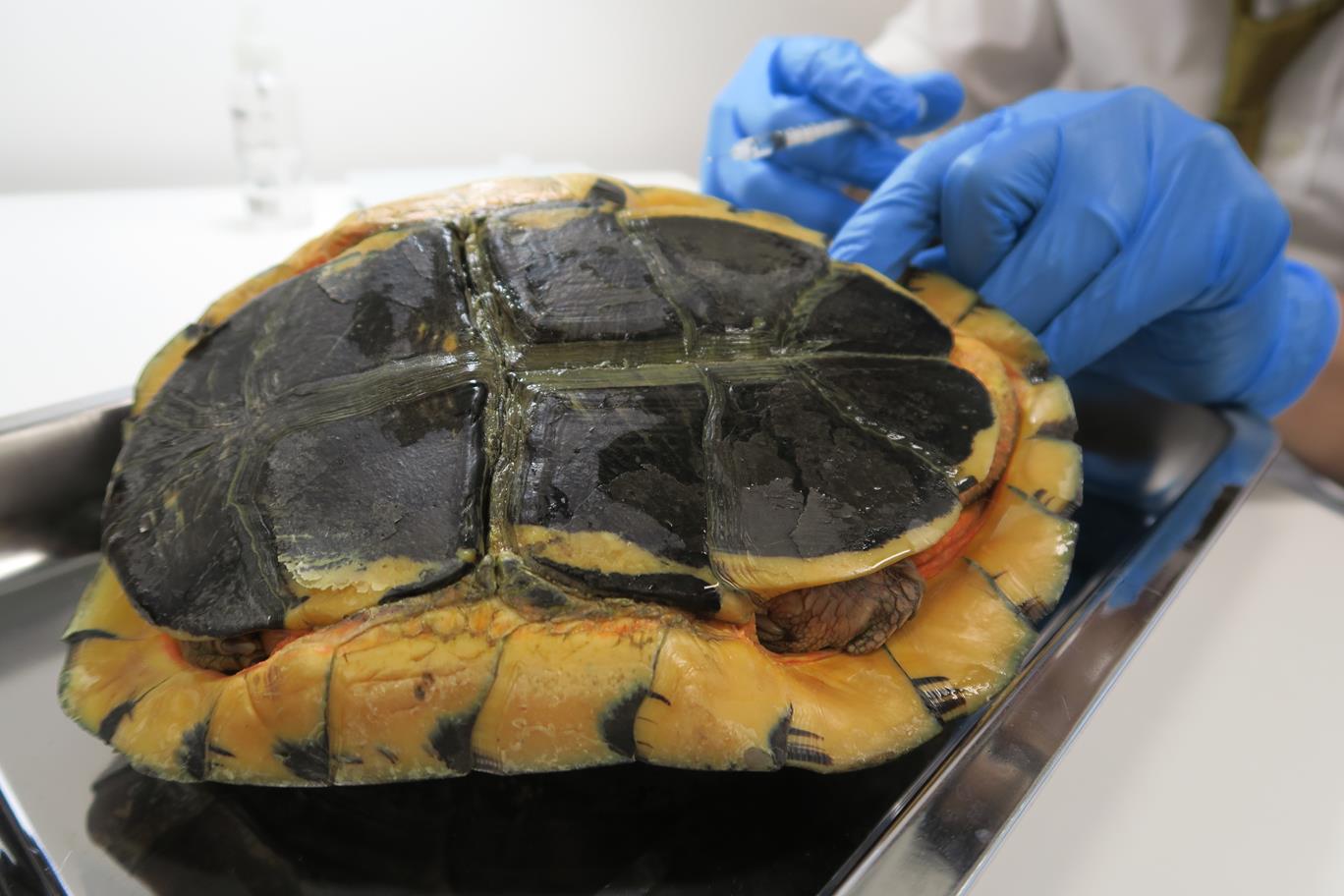
Siu Bo is an over 30 year-old golden Coin Turtle ( Cuora Trifasciata ) living with an old lady. The old lady found Siu Bo’s appetite had dropped for a month and finally became loss of appetite and inactive. She brought her to us, and we found Siu Bo was severely dehydrated and weak.
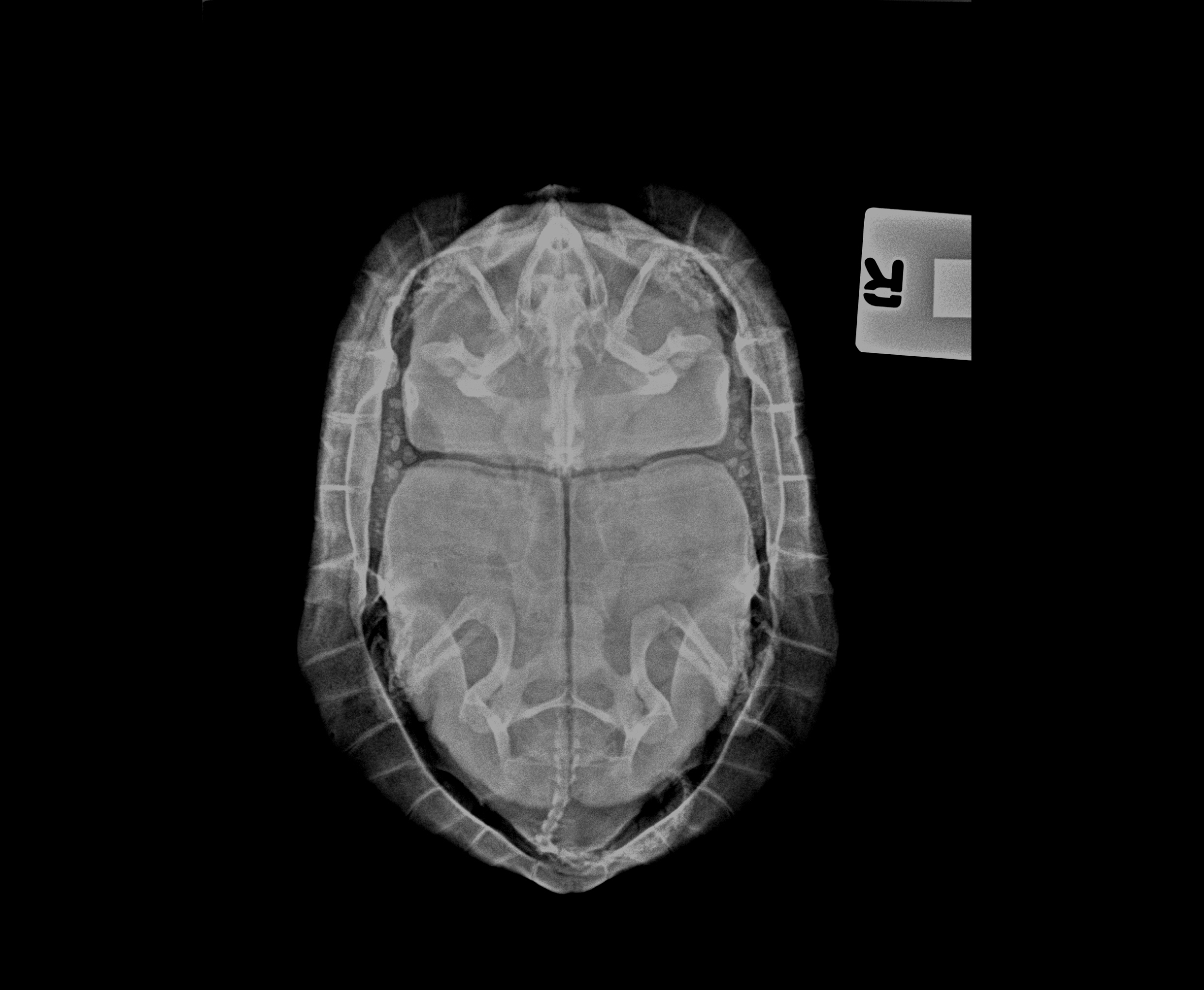
There was a high density oval object inside the caudal region of the coelomic cavity. It could be obstructed in the intestines, urinary bladder or reproductive tracts resulting in loss of appetite.
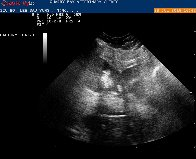
Siu Bo bear the risk of surgical option if failed to respond the course of medication.
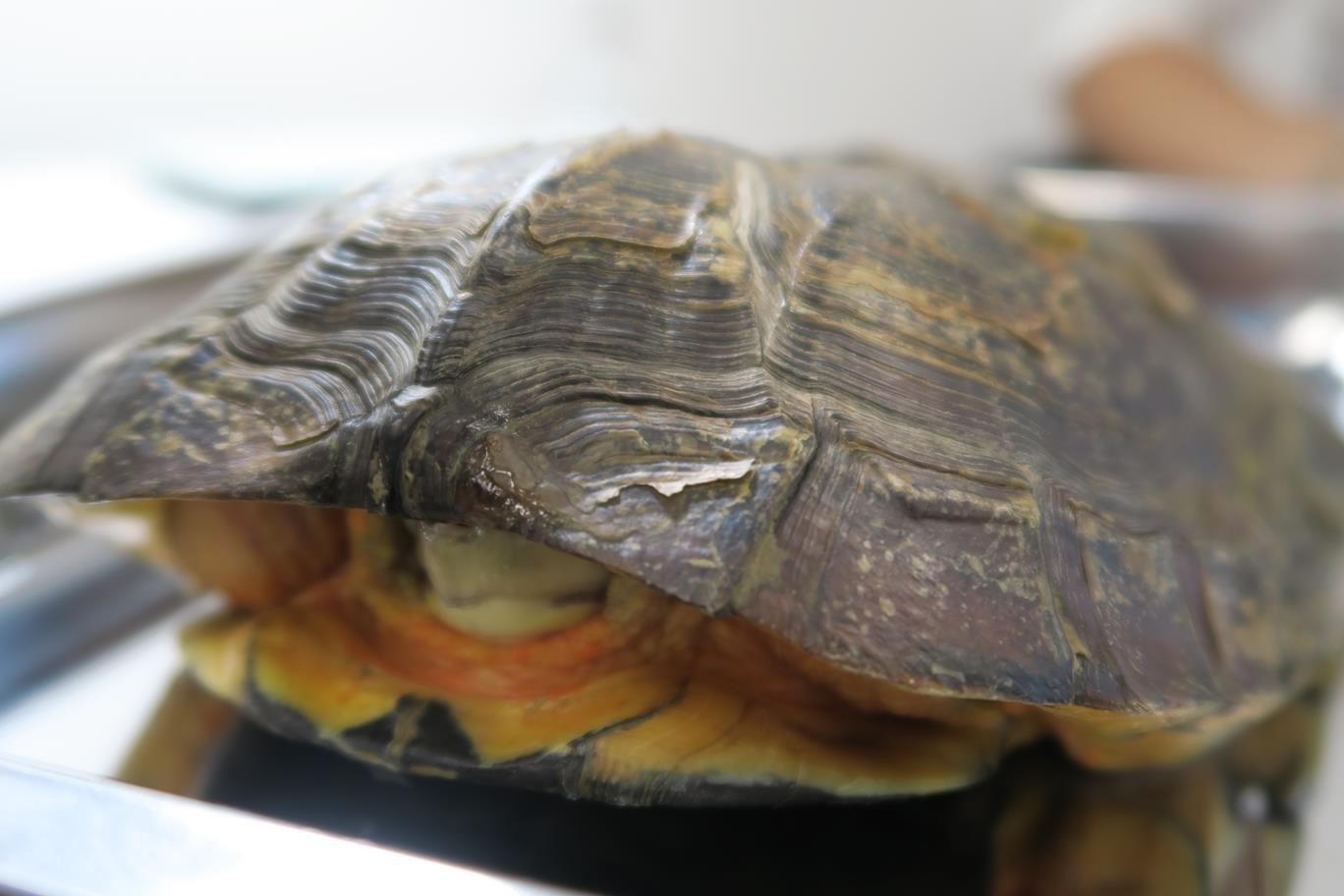

Fortunately, after the intensive care and medical therapy, this oval object was able to pass out. It was a calcified urinary bladder stone. Siu Bo continued the second course of medication and recovered gradually. Siu Bo is now active and eating well again. It’s so blessing.

A correct and good husbandry is very important for turtle health. Please refer to our terrapin husbandry article on the website: http://www.j-vet.com/?id=218 and http://www.j-vet.com/?id=219
Any enquiry about your turtle? Please refer to
寵物小知識

Dog Heart Attack
What is Heart Attack?
Dog heart attacks have been seen in all breeds and are very rare. If you notice symptoms of a heart attack in your dog, keep calm, do not attempt CPR, and contact a veterinarian immediately.
A heart attack, is also called myocardial infarction, happens when blood clot is blocked from reaching the heart muscle (myocardium) resulting in deprived of oxygen and nutrients, the heart muscle dies very quickly and the affected heart chamber is no longer effectively pump blood through the body. Dog heart attacks have been seen in all breeds but are very rare. Genetic predisposition, abnormalities of the heart and underlying medical factors can increase the dog's risk of having a heart attack. Heart attack is an emergency situation and can result in sudden death; therefore, it requires immediately medical treatment.
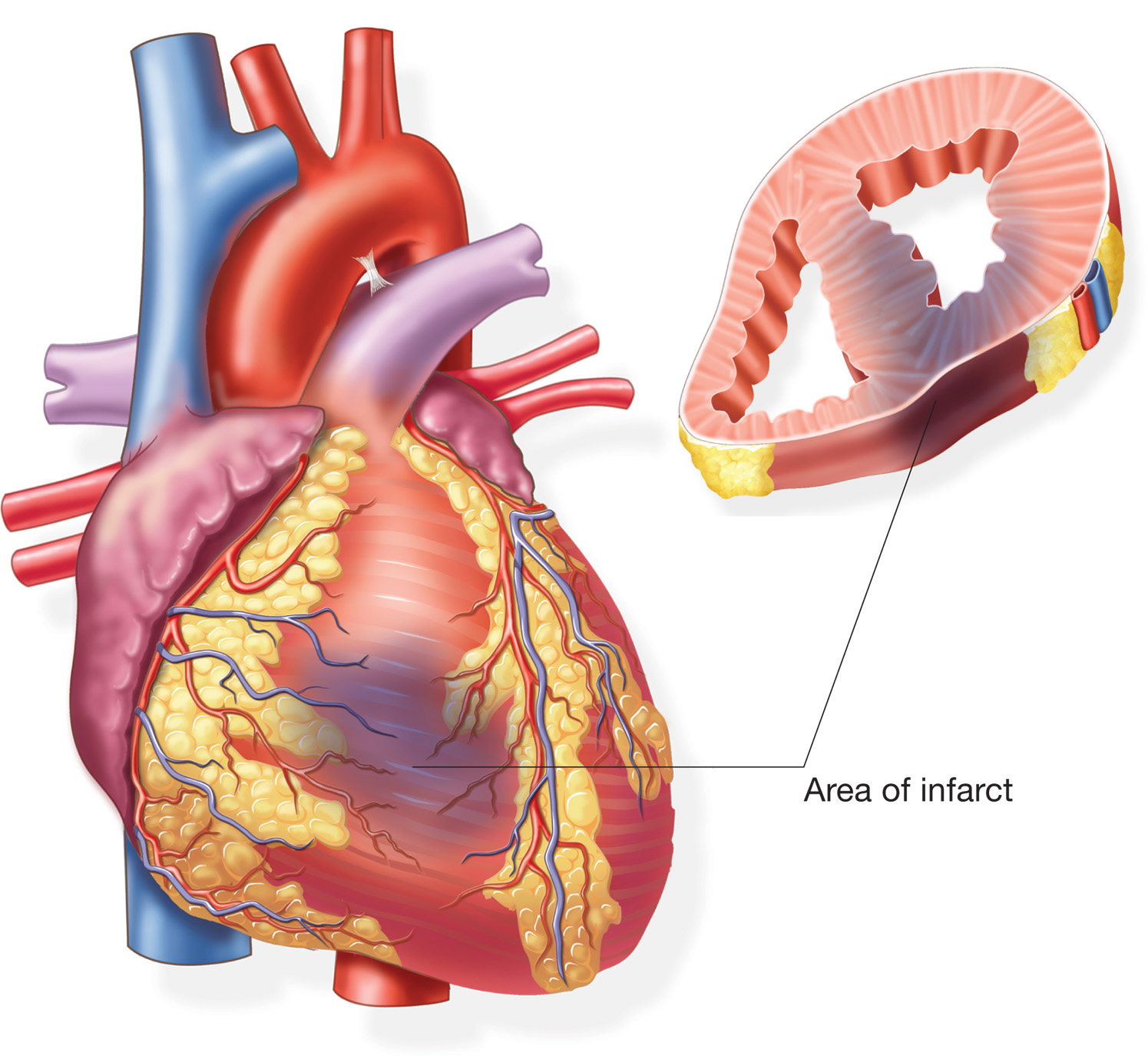
Symptoms of Heart Attack in Dogs
There is little warning for a heart attack event. Sudden collapse may be the first symptom. Symptoms associated with dog heart attack may include:
Slight fever
Vomiting
Panting/difficult breathing
Arrhythmia
Lethargy
Head tilt
Confusion/Anxiety
Stiffness of the forelimbs
Seizure/ collapse
Sudden death without any syndrome
Causes of heart attack in dogs include:
Bacterial infection: Infection in the body such as from periodontal disease can lead to inflammation and blockage of blood flow to the heart muscle.
Vasculitis: Blood vessel inflammation as a result of immune-mediated disease, infection, or other injury to endothelial linings.
Atherosclerosis: Plaque builds up in the arteries, reduces the blood flow or ruptures arteries. Rare in dogs but has been reported in some breeds.
Coronary artery disease: Extremely rare in dogs. Occurs only with severe hypothyroidism associated high serum cholesterol levels.
Hypothyroidism: Thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroxine hormone – responsible for converting food to fuel for the body.
Nephrotic Syndrome: Kidney damage results in loss of protein which involved in preventing blood clot formation.
Tumor: Tumor masses growing on or around the heart vasculature can block blood flow to the heart muscle.
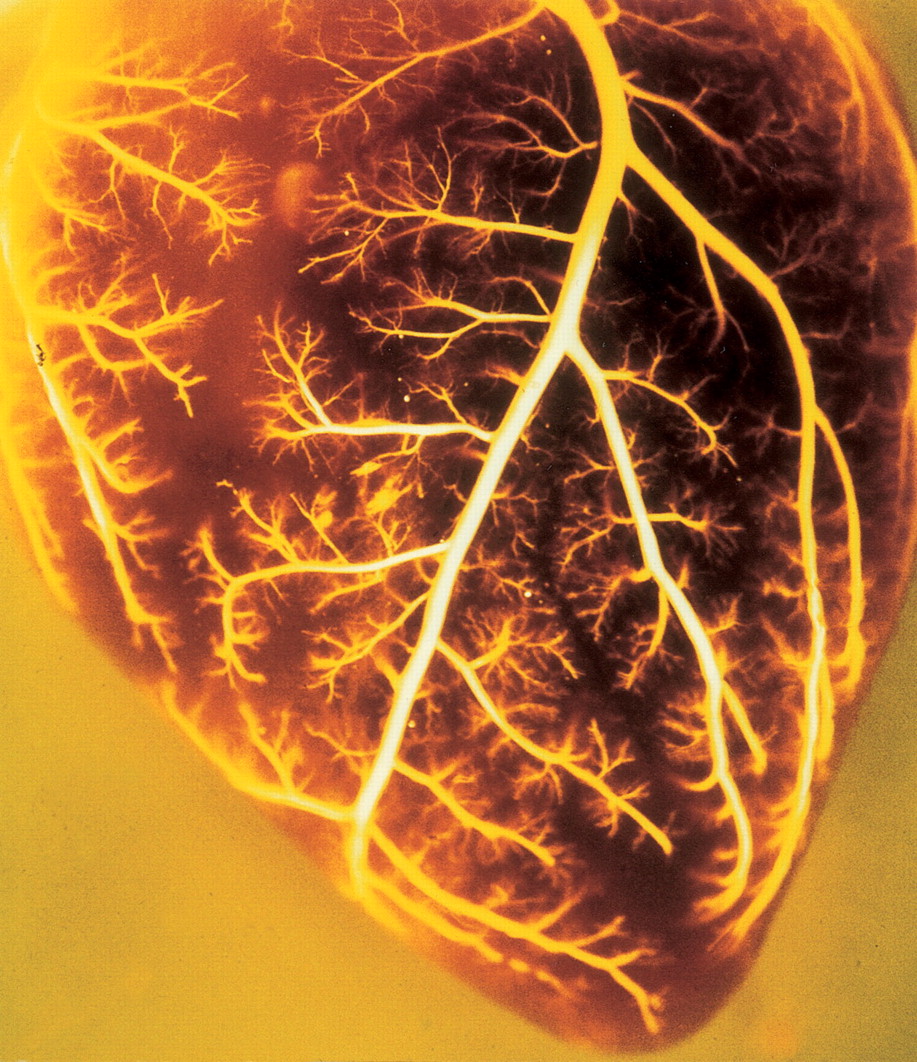
Diagnosis of Heart Attack in Dogs
If you notice symptoms of a heart attack in your pet, please stay calm and carefully wrap the pet in a blanket to calm him. Place your palm on the left side of the chest to feel the heart rate. Count the number of beats in 15 seconds and multiply your answer by 4. This gives you the heart rate. Normal heart rate in dogs will be around 60-140 beats per minute. Call up your regular veterinarian/ 24-hour veterinary hospital to make an emergent appointment if symptoms continue.
If your dog collapses, keep calm and carefully wrap her in a blanket and transport her to the veterinary clinic immediately.
In the hospital, the veterinarian will collect the medical history as to what led up to the symptoms or collapse event. The veterinarian will check the heart for abnormal murmur, pulse, or arrhythmia. Laboratory diagnostic tests are required and they can reveal valuable information as to cardiac function and possible causes of symptoms.
Chest X-ray: Determines size of heart, fluid around heart, possible abnormal masses grow.
Electrocardiography (ECG): Determines cardiac electrical impulses and measures arrhythmias.
Echocardiography: Detects fluid or masses around the heart, heart valve function, heart muscle and pericardial health.
Complete Blood Cell Count (CBC): Determines red and white blood cell count, can detect possible infection.
Biochemistry: Examines kidney and liver function.
Urinalysis: Examines kidney and metabolic function.
Thyroid: Examines thyroid gland function.
If sudden death occurs, dog with heart attack has no signs provided by just examination of the body; therefore, necropsy is the only way to provide evidence of death.
Treatment of Heart Attack in Dogs
Initial treatment involve resuscitation and supportive care, depending on seriousness of the problem. The primary goal is to regain the normal heart activity. Medications such as aspirin may be used to thin the blood for ease of circulation. Hospitalization is necessary to continue monitoring the dog until it is stable.
A variety of medications are available for cardiac disease depending on the primary cause. Surgery may be required to remove any mass that obstructs the blood flow to or from the heart. Thyroid replacement medications are common when hypothyroidism is confirmed. Various diets and medications may provide preventive/supportive care for renal disease if damage is not severe. Antibiotics may prevent further damage to vessels and heart lining resulting from infection or inflammation when endocarditis is suspicious. Anti-arrhythmic medications may be added to correct arrhythmias.
Long-term Management
The potential of recurrence is based on cause of the problem and severity of the myocardial infarction. Surgery and medications can extend the life of the pet for many years when the issue is diagnosed early and treated responsibly. Medications may need to be administered over the remaining life of the pet. Regular check-up is required. Activity restriction may be necessary during the beginning of the treatment.
A Holter monitor or ambulatory ECG is useful to monitor heart health at home for long term monitoring. The heart rhythms are recorded and times of rest versus times of exercise can be reported by the owner.
Any syndrome? Ask a vet for help:http://www.j-vet.com/online-consultation-tc.html
寵物小知識
寨卡病毒 (Zika Virus ) - 寵物
我們的寵物會感染寨卡病毒嗎?
最近,寨卡病毒肆虐,同時亦令寵物主人擔心。
寨卡熱是由寨卡病毒引致,埃及伊蚊(Aedes aegypti)是病毒的主要傳播媒體,其他的伊蚊包括白紋伊蚊也有可能傳播寨卡病毒。其他傳播模式包括胚胎從母體感染、從性接觸傳播。此外,輸血和器官移植都有可能傳播寨卡病毒。
感染者通常沒有可見的徵狀。但有些感染者或會有發燒、斑丘疹、疲勞、結膜炎和頭痛等徵狀。世界衞生組織至今的結論指,懷孕期間感染寨卡病毒是出現包括「小頭症」(Microcephaly)等先天腦部異常的成因。此外,寨卡病毒亦會引發吉巴氏綜合症 。

寨卡病毒的診斷測試主要是從臨床樣本包括血液、唾液、尿液、腦脊液、羊水、精液和乳汁檢測病毒的RNA。然而,病毒逗留在血液的時間很短,可以從血液和唾液檢測到的時間大概是徵狀開始後的三至五天。由第五天起,可以透過血清追縱寨卡病毒的IgM抗體。徵狀出現後的八至十四天內可以用RT-PCR方法檢測病毒。
不幸的是,現階段並沒有寨卡熱的具體有效預防和治療方法。
我的寵物會感染寨卡熱嗎?
現階段,有關狗貓是否會受寨卡病毒影響的研究數據仍然很少。根據美國疾病控制和預防中心,在美國的動物沒有因寨卡病毒導致生病的危機。同時沒有證據顯示寨卡病毒會經由動物傳播或人類將病毒傳給動毒的跡象。寨卡病毒並非新型病毒,早於五十年代已在非洲被發現。目前為止,仍未有動物感染寨卡病毒的個案記錄,但是我們需要更多研究方才可下定論。
我的寵物有機會成為寨卡病毒的傳播媒體嗎?
貓狗有機會透過蚊子叮咬接觸到病毒,但是病毒未必會使動物生病。理論上,他們可以受到感染,但他們未必會表現出明顯跡象,或病毒在貓狗體內的數量遠低於能透過蚊子傳染的所需數量。
預防方法
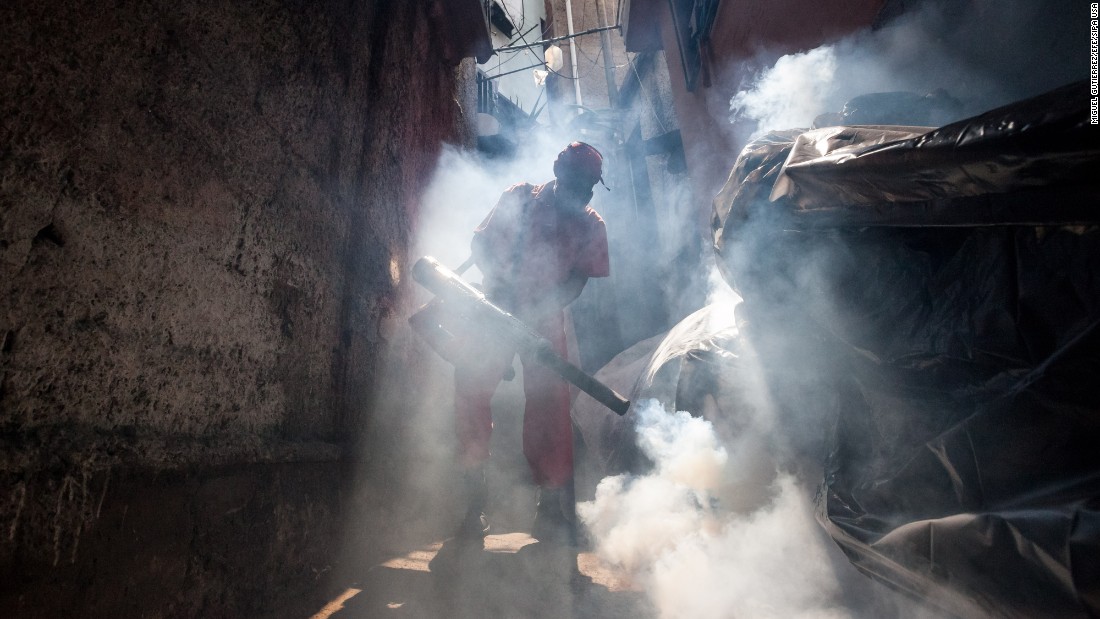

最基本的預防方法就是防治蚊蟲的叮咬。在蚊子活躍的時段(上午的中段、下午至日落時份),可以替在戶外活動的動物塗上驅蟲劑。有些防跳蚤和蝨的噴劑可以防止蚊蟲叮咬,例如適合狗隻用的Power Ultra (Brouwer)。需要注意的是,很多驅蟲劑對貓隻是有毒的。應妥善存放食物及處理垃圾,確保門窗完好無損和清除花盆積水亦有助減少寵物接觸到蚊蟲的機會。
諮詢您的獸醫
如果您仍然擔心寨卡病毒對您的寵物帶來風險,請與您的獸醫聯絡。
有任何問題? 即時向獸醫查詢
寵物小知識
動物幹細胞治療
甚麼是幹細胞,而它是如何幫助我們的寵物呢?
動物幹細胞研究繼續以驚人的速度進行。雖然幹細胞治療的臨床應用可能性仍然遙遙無期,但很多幹細胞治療中心、實驗室或英、美的大學都聲稱成功以幹細胞治療小動物的關節病、脊椎病、腎臟和心臟疾病等等。
幹細胞是指具有顯著發展潛能的原始細胞,它可以在體內化成不同細胞。當幹細胞分裂,每個細胞可保持原有幹細胞的特質,又或變成具專門功能的細胞,例如關節細胞或血細胞。因此,他們經常分裂,以修補和替換受損組織。幹細胞作為再生或修復組織和器官的細胞系。由於這種幹細胞有這種特性,在許多年前,幹細胞治療與發展已是人類和動物再生醫學的一個熱門話題。
動物脂肪有一些間質幹細胞(mesenchymal stem cell),是一種多潛能幹細胞,能夠分裂成不同類型的細胞,包括軟骨細胞、骨細胞、腱細胞、肌細胞和脂肪細胞等。動物幹細胞療法最常見用於退化性關節病/關節炎。
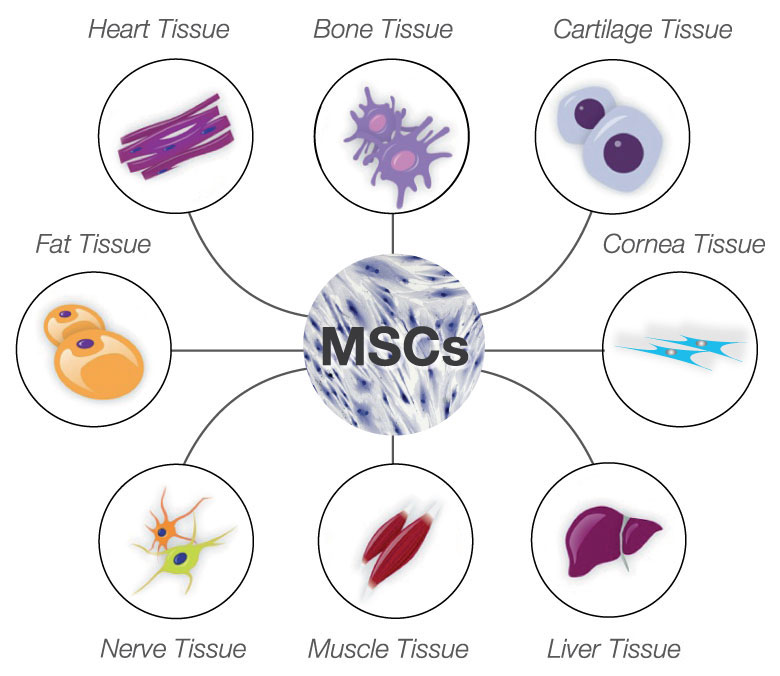
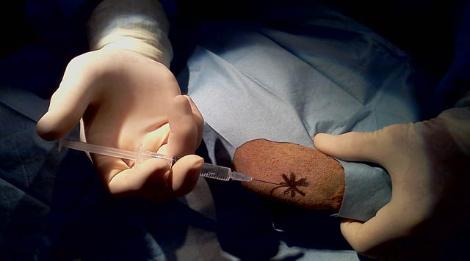
首先,動物在全身麻醉下提取一塊皮下脂肪,接着送到實驗室進行幹細胞培養,以獲得更多間質幹細胞。從培養中得到的幹細胞會被注入到有問題的關節,以增加再生能力和速率。這種療法是自體幹細胞治療,並且可能需要多次注射。幹細胞療法也可用於治療貓的慢性腎功能衰竭和狗的心臟疾病,在這些情況下,會用長導管將幹細胞送到腎臟或心臟。
很多人可能聽說過SVF(Stromal Vascular Fraction) 和PRP (Platelet-rich Plasma)。 SVF指基質血管因子,是其中一種幹細胞治療。然而,SVF所包含的物質尚還未能完全確定,科學家只知道它是由幹細胞和生長因子組成。而生長因子可以減弱發炎反應從而減輕疼痛。它也促進細胞生長以及再生能力。 PRP是指含豐富血小板的血漿,它只有生長因子,常用於骨科和創傷護理。製作SVF和PRP相對容易,需時較短。一些動物醫學製造商甚至開發了in-house kit以製造SVF和PRP。
幹細胞治療領域仍然是一個新興產業,其長期影響仍然備受關注。幹細胞治療最令人擔心就是其潛在致癌的風險,正是因為它能促進細胞生長。幹細胞和癌細胞具有一些相同的特徵,例如較長的生命周期,抵禦細胞凋亡的能力,類似的生長調節和控制機制以及容許複製的時間較長。例如,在癌症下,大量的生長因子可加速癌細胞的生長。幹細胞治療缺乏監管,故此應用並未有完善的標準可遵循。
我們相信,幹細胞治療是創新且具醫療效果。我們已經在私人診所和海外大學看到許多成功的案例。為了鞏固幹細胞治療的發展,我們需要更多關於幹細胞治療的生物機制研究、分辨細胞的表徵及質量和臨床應用結果。現階段,對於幹細胞療法和機制的知識仍然十分有限。希望在不久的將來,幹細胞治療能夠有效且安全地幫到更多動物及人類。
有任何問題? 即時向獸醫查詢